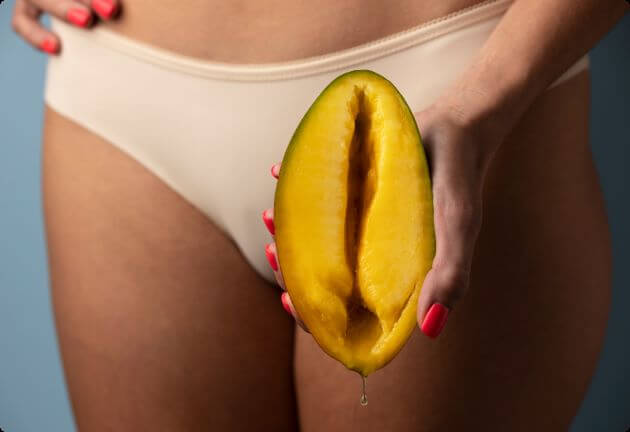
Vaginal discharge is a natural process of the female body. It’s a topic that is sometimes considered taboo, but it’s crucial to openly discuss: what causes vaginal discharge, when is it normal? And when does it indicate potential health issues? In this blog, we’ll teach you everything about white, yellow, green and brown vaginal discharge: what is considered normal? And what isn’t? How does vaginal discharge change throughout the menstrual cycle? And if you notice a change, what does it mean? Plenty to discuss, let’s get started!

What is vaginal discharge?
Vaginal discharge is the natural process where fluid is expelled from the vagina. This fluid is produced by glands in the walls of the cervix and vagina. The composition of the discharge can vary depending on the menstrual cycle and hormonal changes.
The purpose of discharge is to keep the vagina clean and hydrated, prevent infections, and aid in reproduction by guiding sperm to the egg. It’s normal to have a small amount of discharge daily, as long as it doesn’t cause discomfort or is accompanied by unpleasant odors or itching.
Vaginal discharge is typically white-yellow to translucent in color. When it dries in your underwear, it can become slightly lumpy or granular.


It’s important to note that discharge is usually not odorless but rather has a mild, acidic scent due to healthy bacteria present in your vagina. If you have more discharge than usual or if its color has changed, this could be a normal part of your cycle or an indication of an underlying condition. Keep reading to find out how to distinguish between the two.
Types of Discharge in the Menstrual Cycle
Throughout the menstrual cycle, the quantity, composition, and color of vaginal discharge can vary, influenced by hormonal changes occurring in different phases of the cycle.




Follicular Phase:
After your menstruation ends, the follicular phase begins. During this phase, estrogen levels gradually rise. Under the influence of estrogen, vaginal discharge typically becomes thinner, clear, and elastic. Some women describe this as mucus-like discharge.
Ovulation:
During ovulation, the amount of discharge often reaches its peak. The fluid becomes clearer, thinner, and more elastic than in other phases of the cycle. This aids in facilitating the path for sperm and increasing the likelihood of fertilization.
Luteal Phase:
After ovulation, estrogen levels decrease, and progesterone levels rise. This can result in thicker, more cloudy discharge.
Menstruation:
If no pregnancy occurs, menstruation begins. Up to several days after menstruation, there may be brown vaginal discharge.
How much discharge is normal?
The amount of vaginal discharge considered normal can vary from woman to woman. Generally, a small amount of daily discharge is considered normal and healthy. If the discharge doesn’t cause discomfort and has no unpleasant odor, it is usually not a cause for concern.
The quantity and color of vaginal discharge can change under the influence of hormones (such as contraceptive pill usage, pregnancy, menopause, or different phases of your menstrual cycle), infections, or stress. If you suddenly experience a significant increase in discharge, a change in color, it becomes strongly odorous, or you have other symptoms, there may be an underlying condition. More information on this is provided below.



Vaginal discharge: color and meaning
As mentioned earlier, the color of vaginal discharge changes throughout the menstrual cycle or under the influence of other hormonal shifts, which is normal. Vaginal discharge can also vary in quantity and color during periods of stress or illness. However, an increase in discharge or changes in its color may indicate an underlying condition or health issue.
To differentiate between these types of discharge, below is a list of all types of vaginal discharge and their meanings:


- White
A milky white or light yellow discharge is usually normal, especially at the beginning or end of the menstrual cycle. Thick, white discharge resembling cottage cheese may indicate a yeast infection, such as Candida. This may be accompanied by clumpy discharge, itching, redness, or a burning sensation during urination.
- Transparent
Clear and watery discharge is common during ovulation and is considered normal.
- Cloudy
Cloudy discharge may suggest an increased number of cells or bacteria in the vagina, indicating an infection.
- Yellow or Green Vaginal Discharge
Yellow or green vaginal discharge may be a sign of an infection, such as an STD like chlamydia or gonorrhea. When accompanied by abdominal pain, fever, and pain during sexual activity, it may indicate PID (pelvic inflammatory disease), which can result from an STD, childbirth, or intrauterine device placement. In such cases, you should consult a doctor for further examination.
- Brown or Pink Discharge
Brown or pink vaginal discharge may occur at the beginning or end of menstruation and is usually normal. Mixing a small amount of blood with regular vaginal discharge can result in dark vaginal discharge. Brown discharge may also be normal for individuals using contraceptive pills, known as spotting. This should resolve on its own, but if it persists, it’s advisable to consult your doctor for further investigation. If brown or pink discharge is accompanied by other symptoms like abdominal pain, itching, or fever, seeking medical attention is important, as it could indicate an infection.
- Gray
Thin, gray discharge with an unpleasant fishy odor may indicate bacterial vaginosis, an overgrowth of bacteria in the vagina. If you experience these symptoms, it’s recommended to schedule an appointment with your doctor.
Related tests

What to do about vaginal discharge?
However, if you notice changes in your vaginal discharge, it’s essential to be vigilant about other symptoms such as itching, an unpleasant odor, abdominal pain, or irritation. If you experience any of the mentioned symptoms and wonder about their cause, Easly offers multiple test kits that allow you to easily and reliably determine at home whether your symptoms may be caused by any of the aforementioned conditions. Suspecting a possible STD? Take the Easly STD test guide and find out which test we recommend for your specific situation.

Conclusion
Vaginal discharge is a normal and healthy aspect of the female body. It changes throughout the menstrual cycle and under the influence of other hormonal shifts, leading to variations in color and consistency. While some discharge is normal, it is crucial to be vigilant about changes that may indicate health issues. Always consult a doctor if you are concerned about alterations in your vaginal discharge, especially if they are accompanied by other symptoms.