Cortisol is an indispensable hormone in the body. However, a shortage or surplus can cause serious complaints. Despite the fact that cortisol is also called the stress hormone, an elevated cortisol level does not necessarily indicate stress. Enough reasons to dive into the world of this hormone and list the symptoms of too high or too low cortisol.
What is Cortisol?
Cortisol is a hormone produced in the adrenal cortex. It is a versatile substance involved in numerous processes within the body. For example, cortisol ensures that your body is alert during stress, which is why it is also called the stress hormone. Additionally, cortisol plays a role in regulating the immune system by helping to suppress inflammatory reactions. It also promotes the conversion of proteins and fats into glucose, raising blood sugar levels.

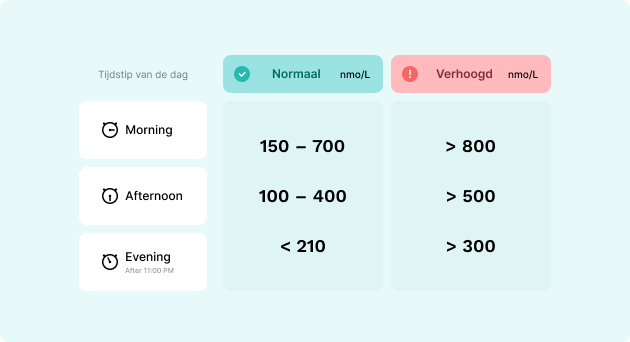
Cortisol Normal Values
Cortisol levels fluctuate throughout the day. In the morning, when many people are most active, cortisol levels rise. Late at night, while sleeping, your cortisol levels drop back to lower values. The table below generally shows the normal cortisol values:
Symptoms of High Cortisol
A wide variety of symptoms can indicate high cortisol levels. Some of these symptoms may also be related to other conditions. To be certain, only a cortisol test will suffice. What are the common symptoms of high cortisol levels? Frequently mentioned symptoms include poor sleep, fatigue, weight gain, high blood pressure, loss of muscle strength, irregular menstrual cycles, and weakened immunity, making you prone to illness.
Additionally, some people complain of forgetfulness, heartburn, nausea, or diarrhea. This list of possible symptoms is not exhaustive, as decreased libido, nervous feelings, sugar cravings, and weight gain, particularly in the abdominal area, can also be related to elevated cortisol levels.
Causes of High Cortisol Levels
Cortisol production can be influenced by external factors or originate within the body. For example, the adrenal cortex itself may produce too much cortisol, known as Cushing’s syndrome. Sometimes, the cause of this syndrome is a benign tumor in the pituitary gland or a benign or malignant tumor in the adrenal glands. In such cases, surgery may be considered. Medications containing cortisol can also logically affect your cortisol levels, as can long-term use of the hormone adrenocorticotropic (ACTH).
External factors also play a role in causing high cortisol levels. Stress, trauma, and temperature stimulate cortisol production. If an initial test indicates elevated cortisol, the doctor will conduct additional investigations to determine the exact cause.
Related tests



Cortisol Deficiency: What If You Have It?
You might also experience a cortisol deficiency in your body. This is called hypocortisolism (also known as Addison’s disease). This deficiency may result from adrenocortical disorders, abnormal pituitary behavior, or long-term cortisone use. However, hypocortisolism is very rare: only about one in 100,000 people will be affected by this condition.
The symptoms of cortisol deficiency are not very specific: fatigue, lack of energy or appetite, weight loss, or a bronze-like discoloration of the skin. Ultimately, your doctor will need to perform blood tests to confirm hypocortisolism. If so, your doctor will attempt to compensate for the deficiency with cortisone. The dosage depends on how much your body needs.

Tips & Tricks for Lowering Cortisol
If your cortisol is too high for an extended period, it can have severe consequences. It is crucial to take measures if your cortisol level is too high. How can you lower your stress hormones? If you require medical treatment, you should discuss this with your doctor. However, there are also steps you can take yourself. We have listed the most important tips for you:
- Ensure you get enough sleep. During sleep, your cortisol level decreases. A rested body is more resistant to stress.
- Consume omega-3 fatty acids. Why? Omega-3 lowers cortisol levels and helps you cope better with stress. Foods rich in omega-3 include mackerel, flaxseed oil, nuts, and seeds.
- Exercise regularly. Physical activity increases your resistance to stress and lowers your cortisol levels. But don’t overtrain yourself, as it can stress your body.
- Lower cortisol through nutrition: eat less sugar. Cortisol plays a role in converting sugars into fats. The less sugar you eat, the less your body is stimulated to produce cortisol.
- Drink enough fluids. Stress can cause dehydration. Ensure adequate fluid intake, especially during exercise. Research shows that black tea lowers cortisol levels. So, consider making a cup of tea in the kitchen?
Miracles don’t exist. But the above tips can help you along the way. Unless genetic or medical conditions underlie your high cortisol level, getting enough healthy sleep, moderating your sugar intake, and reducing stress factors will go a long way.




Measuring Cortisol Levels
It is clear: cortisol plays a crucial role in various body processes that can significantly influence your state of mind. Moreover, the long-term effects of excessively high cortisol levels are apparent. It is all the more important to closely monitor your cortisol levels. Easly has developed a test that measures your cortisol. Simply from your own home. The home test contains everything you need. After sending the sample to our laboratory in the return envelope, you can view the result online within a few days.