Vitamin D plays a crucial role in maintaining good health. It helps with calcium absorption. It aids in both calcium and phosphorus absorption, supports a strong immune system, and promotes the health of bones and teeth. However, there is often confusion about the different forms of vitamin D, particularly Vitamin D2 and D3. In this blog, we will discuss the difference between Vitamin D, D2, and and D3, the benefits of both, and how to ensure you get enough of them.


What is vitamin D?
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin that helps with the absorption of calcium and phosphorus, essential minerals for healthy bones and teeth. In addition, it plays an important role in other bodily processes. Not only does it support bone health, but it is also involved in immune system function, muscle function, and mental health.
Clearing up the confusion between Vitamin D and D3
A lot of people mix up “Vitamin D” and “Vitamin D3.” Here’s the deal: “Vitamin D” is the general term for both D2 and D3. But D3 is the form that your body uses more effectively, which is why it’s the go-to option for most people when it comes to supplements. So if you hear someone say “Vitamin D,” they usually mean D3 since it’s the better option for raising your Vitamin D levels.
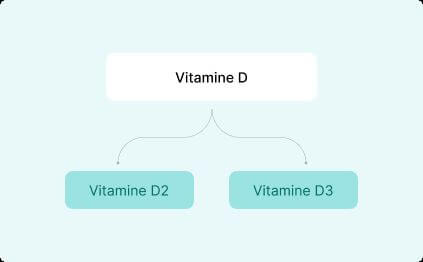
So, here’s where it gets a bit more specific: there are two main forms of Vitamin D.
- Vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol) – This type mostly comes from plants and fortified foods. (Fortified just means that extra nutrients, like Vitamin D, are added to foods that don’t normally have them). Some examples include plant-based milks (like soy or almond), breakfast cereals, and even certain orange juices. Vitamin D2 isn’t as good at raising your Vitamin D levels compared to D3.
- Vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol) – This one is produced by your skin when you’re out in the sun and is found in animal-based foods like fatty fish (think salmon or mackerel), egg yolks, and liver. D3 is better at increasing your Vitamin D levels, which is why most experts recommend it if you’re taking supplements.

Now, once you’ve gotten Vitamin D (either from the sun or food), your body has to activate it. First, your liver changes it into a storage form called calcidiol. Then your kidneys step in and convert it into the active form, calcitriol, which is what your body uses to help with all those important functions like bone health and immune support.
How vitamin D helps your health:
- Strengthens your immune system: Vitamin D helps your body fight off infections and lowers inflammation. For example, if your Vitamin D is too low, you might find yourself getting sick more often.
- Keeps your muscles working well: Having enough Vitamin D can help keep your muscles strong and lower the risk of falls, especially as you get older.
- Boosts mental health: Low Vitamin D levels have been linked to mood issues like depression. This is especially true for people who don’t get enough sunlight during the winter months, leading to conditions like Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD).
- May support heart health: Some research suggests Vitamin D might help with things like regulating blood pressure, which is important for keeping your heart healthy.



Vitamin D2 and D3 further explained
Vitamin D2 is another form of Vitamin D, which mainly comes from plant-based sources, such as mushrooms. Although Vitamin D2 contributes to raising Vitamin D levels, it is less potent and less effective than Vitamin D3.. Vitamin D2 and D3 forms are chemically different and also differ in origin and effectiveness in our body. Below, we explain the differences in simple terms and why it’s important to know which form you are taking.
1. Chemical structure and origin:
The main differences between Vitamin D2 and D3 begin with their source. Vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol) is produced in the skin when exposed to sunlight, specifically UVB rays. This is the form of Vitamin D that the body naturally produces, and it is also found in animal products such as fatty fish (salmon, mackerel), cod liver oil, eggs, and fortified foods.
Vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol) comes from plants and fungi. You can primarily find it in mushrooms exposed to UV light. It is produced less frequently in the body and is often found in fortified foods such as certain plant-based milks and cereals.


2. Effectiveness: What works better?
Although both Vitamin D2 and D3 can help raise your body’s vitamin D levels, they are not equally effective. Scientific research shows that Vitamin D3 is much more efficient at raising and maintaining blood vitamin D levels. Vitamin D3 also remains active in the body longer, meaning it offers more long-term benefits. This is because the body stores and uses Vitamin D3 better when needed.
Vitamin D2 can still be useful, especially for people who do not consume animal products, such as vegans. It is often used in plant-based supplements and fortified foods. However, if you have the option and want to ensure that your vitamin D levels remain optimal, Vitamin D3 is usually the better option. Studies have shown that D3 is up to three times more effective at raising vitamin D levels than D2.

3. Different roles in the body
Although both forms can contribute to bone health and support the immune system, there are small differences in how they are used by the body. Vitamin D3, the form that the body naturally produces, seems to work better at maintaining stable blood levels over the long term. This means it is more effective at preventing conditions related to vitamin D deficiency, such as osteoporosis and muscle weakness.


Vitamin D2 is often used in medical supplements or food fortification, especially in countries where vitamin D deficiency is a common problem. It can be effective, but since the body uses and stores it less efficiently, you may need to take D2 more frequently or in higher doses to achieve the same results as D3.
4. Which form should you choose?
If you choose a vitamin D supplement, it is important to know which form you are taking. For most people, Vitamin D3 is the best choice because it is more effective and works longer. This is especially important during the winter months when sunlight exposure is limited and the risk of deficiency is higher.
For people who do not want to use animal products, there are also plant-based D3 supplements available, made from lichen, which are just as effective as the animal-based variant.



Which is better: D2 or D3?
In most cases, Vitamin D3 is considered the better option, especially when it comes to raising and maintaining healthy vitamin D levels. Vitamin D3 is absorbed faster and stays in the body longer, making it generally more effective.
However, D2 is more commonly used in fortified foods and supplements for vegans, as it is plant-based. For those without vegan dietary preferences, D3 is typically recommended.

How to get Vitamin D?
Getting enough vitamin D can be a challenge, especially during the winter months when sunlight exposure is limited. Here are some ways to get both Vitamin D2 and D3:
Vitamin D2 sources
- Fortified plant-based milk
- Mushrooms exposed to UV light
Vitamin D3 sources
- Fatty fish such as salmon, mackerel, and tuna
- Cod liver oil
- Fortified foods such as dairy products and cereals
- Supplements


In addition, symptoms of a vitamin D deficiency, such as fatigue, weak bones, or muscle pain, may be a sign that you are not getting enough vitamin D. Read more about these signs in our blog on symptoms of vitamin D deficiency.
How much vitamin do you need per day?
The recommended daily intake of vitamin D, and more specifically Vitamin D3, varies depending on age, health, and sunlight exposure. In general, adults are advised to get between 10 and 25 micrograms (400-1000 IU) of Vitamin D3 per day. This range better reflects common recommendations across different health organizations.. Vitamin D3 is the most effective form of vitamin D, especially for raising blood levels of active vitamin D. Vitamin D2 is sometimes used in supplements but is less effective at raising vitamin D levels compared to D3, so the recommended dosage for D2 may need to be increased, often by about 30-40%, depending on the individual’s needs.



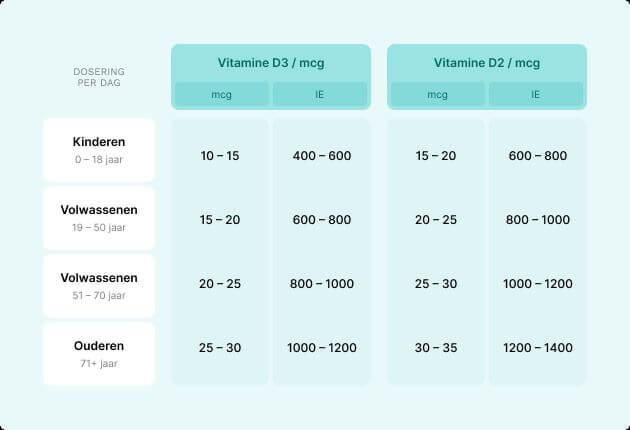
The vitamin D requirements by age group differ:
- Children (0-18 years): For the development of strong bones and teeth, it is recommended that children take 10-15 micrograms (400-600 IU) of Vitamin D3 daily, especially if they get little sunlight or have dark skin. Vitamin D2 can also be used, but the dosage should be higher, around 15-20 micrograms (600-800 IU) per day..
- Adults (19-50 years): In this age group, 15-20 micrograms (600-800 IU) of Vitamin D3 per day is sufficient to support bone, muscle, and immune health, especially for those who spend little time outside or have a busy lifestyle. If you choose Vitamin D2, a slightly higher dose of 20-25 micrograms (800-1000 IU) is needed.
- Adults (51-70 years): As we age, the skin’s efficiency in producing Vitamin D decreases. People in this group often need 20-25 micrograms (800-1000 IU) of Vitamin D3 per day to maintain bone density and reduce the risk of osteoporosis. Vitamin D2 supplements may need to be increased to 25-30 micrograms (1000-1200 IU).
- Seniors (71+ years): For older adults, a higher dose of 25-30 micrograms (1000-1200 IU) of Vitamin D3 per day is often recommended, as they are at increased risk of fractures and muscle weakness due to a deficiency of vitamin D. Vitamin D2 may require a dose of 30-35 micrograms (1200-1400 IU) per day in this group.
Vitamin D3 is generally recommended for all age groups because it is better absorbed and works more efficiently than Vitamin D2. However, both forms can be effective, provided the correct dosage is used. If you are using Vitamin D2 supplements, you should adjust the dosage to achieve the same effect.


Because too little or too much vitamin D can have adverse effects, it is important to test your vitamin D level regularly. Excessive intake (above 100 micrograms or 4000 IU daily) can lead to side effects such as nausea, vomiting, and even bone problems. Therefore, it is crucial to test your vitamin D level before taking supplements to determine the appropriate dosage. By testing your vitamin D level with Easly’s Vitamin D test, you can accurately determine how much vitamin D your body needs and avoid both deficiency and excess. This ensures safe and effective use of supplements. Always consult a doctor before taking high doses of vitamin D supplements.
Additionally, you can rely on our partner Allfit for a wide range of supplements. As an expert in health and nutrition, they offer the perfect assortment to keep you healthy this winter. They provide products of the highest quality, tailored to your personal needs, ensuring you are optimally prepared for the cold months.
Conclusion
Vitamin D, in both D2 and D3 forms, is essential for maintaining strong bones, a healthy immune system, and overall well-being. Although both forms offer benefits, Vitamin D3 is often considered superior due to better absorption and longer-lasting effects in the body.. Make sure to get enough vitamin D, especially during the winter months, through sunlight, food, or supplements to prevent a deficiency.