Chlamydia is one of the most prevalent sexually transmitted infections (STIs) worldwide, significantly impacting public health. In the Netherlands, chlamydia is also a commonly reported infection; in 2022, the number of positive chlamydia tests increased significantly compared to previous years. It is crucial to understand that chlamydia is a stealthy infection that does not always present symptoms, leading people to be unaware of their infection. This contributes to the rapid spread of the infection, particularly among young sexually active individuals.


As you can understand, the lack of symptoms makes regular screening and awareness all the more crucial. By reading this blog, you will gain a better understanding of chlamydia and its impact on health. In this blog, you will learn everything about its contagious nature, potential symptoms, treatment, and the consequences of an untreated chlamydia infection.
What is Chlamydia?
Chlamydia is a common sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the bacterium Chlamydia trachomatis. It affects both men and women and can impact various parts of the body, including the genital organs, anus, throat, and eyes. But how does one contract chlamydia? Chlamydia can be transmitted through sexual contact with an infected person. Unprotected sex, including vaginal, anal, and oral sex, can result in the transmission of chlamydia. The likelihood of infection with each unprotected sexual encounter is 10%. It’s important to note that chlamydia cannot be transmitted through kissing. It is noteworthy that even in the absence of noticeable symptoms, the infection can still be transmitted.
Following exposure to Chlamydia trachomatis, symptoms may take several days to weeks to manifest; this period is known as the incubation period. However, chlamydia can be quite deceptive as it often causes no noticeable symptoms, leading individuals to be unaware of their infection. This may result in the infection going unnoticed and being unknowingly passed on to others. Hence, it is often referred to as a “silent” infection. But is chlamydia dangerous? We will delve deeper into this question in this blog after discussing the symptoms for both men and women.

Chlamydia symptoms in men and women
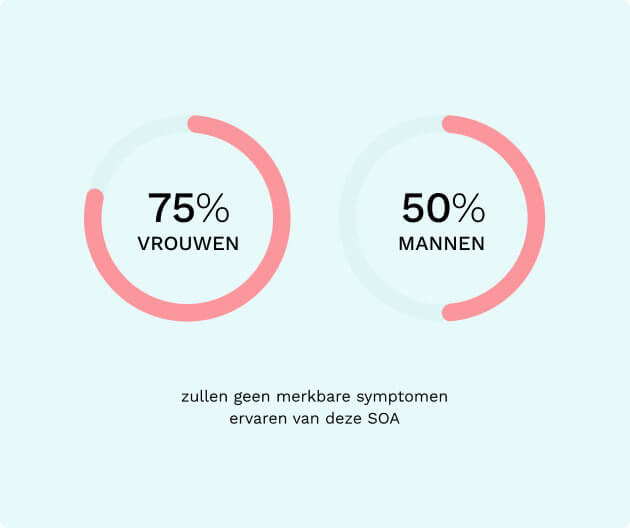
As mentioned above, an infection with chlamydia does not always present symptoms: 70-80% of women and 50% of men may not experience noticeable symptoms of this STI, even though they are contagious and may face consequences from an untreated chlamydia infection. However, you may still experience symptoms upon being infected with the chlamydia bacterium. After contracting the infection, it takes several days to weeks before you notice any symptoms. Below are the symptoms for both men and women:
Chlamydia Symptoms in Women
Women may experience the following chlamydia symptoms:
- Altered vaginal discharge
- Pain during urination
- Vaginal bleeding after sexual intercourse
- Vaginal bleeding between menstrual periods
- Pain during sexual intercourse
Chlamydia Symptoms in Men
Men may experience the following chlamydia symptoms:
- Pain or burning sensation during urination
- Discharge from the penis
- Testicular pain




It is important to reiterate that chlamydia can also be asymptomatic in both genders. Therefore, regular chlamydia testing is crucial if you are sexually active. This can be done easily and reliably through our chlamydia self-test. If you want to rule out other STIs as well, at Easly, we offer five different STI packages. If you want to determine which STI package suits your situation best, take the Easly STI Test Advisor. We also have an extensive blog discussing other common STIs.
Related tests


Chlamydia treatment
Is chlamydia dangerous? In 50% of all untreated infections, chlamydia may resolve without any treatment. However, untreated chlamydia can potentially have severe consequences for both men and women. Women who have had a chlamydia infection are at an increased risk of developing pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), where the uterus, ovaries, or fallopian tubes can become inflamed. This can result in illness, fever, and abdominal pain, especially during intercourse. When a chlamydia infection remains untreated, there is a very small chance of fertility problems. While it may take a bit longer to conceive after a chlamydia infection, looking at the statistics, women who have had a chlamydia infection have as much chance of getting pregnant as those who haven’t. The risk of fertility problems increases when there are multiple or severe chlamydia infections or when someone has had PID multiple times. Overall, the chance of becoming infertile due to chlamydia is very small.



In men, an untreated chlamydia infection can also have consequences. It may lead to epididymitis, inflammation of the epididymis, causing the testicle to become red, swollen, and very painful. It can also temporarily affect the quality of a man’s sperm, which is often temporary and fully recovers.
Fortunately, chlamydia can be effectively treated with antibiotics. The primary treatment is through a course of antibiotics. It is essential to complete the entire course as prescribed, even if symptoms improve or disappear.
When is chlamydia gone after treatment? After completing the prescribed antibiotic treatment, chlamydia is typically cleared from the body within one to two weeks. It is crucial to abstain from sexual contact for a week after starting treatment or until symptoms have completely resolved.
What if Chlamydia persists after treatment?
In some cases, chlamydia may persist or recur even after completing the prescribed treatment. This could be due to factors such as reinfection, incomplete treatment, or an incorrect diagnosis. If symptoms persist or reoccur, it is important to consult a healthcare provider for further evaluation and explore potential alternative treatment options.

Conclusion
Chlamydia is one of the most common sexually transmitted infections. Due to its asymptomatic nature, chlamydia can spread rapidly. This poses potentially severe consequences, as an untreated chlamydia infection carries a small risk of serious infections and fertility problems. Therefore, regular testing for this STI is crucial. Fortunately, chlamydia is effectively treatable with a course of antibiotics. Regular testing, practicing safe sexual behavior, and open communication with sexual partners are essential for prevention and early detection of chlamydia. Remember that seeking medical advice is important if symptoms persist or recur after treatment. Stay informed, stay safe!