A slow or overactive thyroid can cause unpleasant symptoms and eventually lead to significant health problems. But what is the function of the thyroid in the body? And what are the most common thyroid problems and symptoms? We present the most important facts for you and explain how you can identify and (have them) rectify thyroid problems.
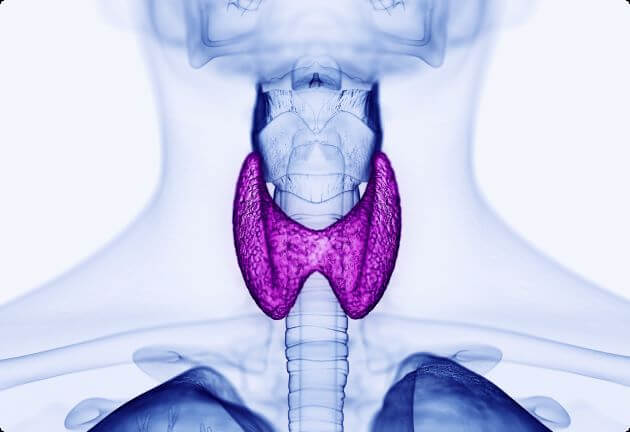
Explaining the thyroid
The thyroid is located at the front of the neck. It is shaped like a butterfly and consists of two lobes with follicles, in which the thyroid hormones T3 and T4 (also known as thyroxine) are produced. The C cells between the follicles of the thyroid also produce a hormone: calcitonin. This doesn’t happen automatically: the pituitary gland and the hypothalamus, two important structures in the brain, regulate the functioning of the thyroid. They do this by secreting hormones that stimulate the thyroid to function.
The T3 and T4 hormones produced in the thyroid play an important role in metabolism and growth. For example, the T4 hormone ensures that your body can extract energy from food. Calcitonin also has an important function. It inhibits the breakdown of bone tissue. If your thyroid is out of balance, you will notice it directly, and it can sometimes be difficult to understand the cause of your symptoms.
Thyroid problems & symptoms
A thyroid that produces too much hormone (hyperthyroidism) or too little (hypothyroidism) causes symptoms. In a slow-working thyroid, the symptoms all have to do with your energy metabolism. You may feel tired, cold, have thick eyelids, or suddenly gain weight. Sometimes your intestines can also become constipated.
With a thyroid that works too fast and therefore produces too many hormones, you can sometimes be tired as well. But the other symptoms indicate hyperactivity of the body: palpitations, tremors, sweating, feeling quickly irritated or restless, or having diarrhea. With a fast-working thyroid, you don’t gain weight, but you can lose weight.
A thyroid can also swell. Such an enlarged thyroid is called a goiter. You may then have difficulty swallowing or have breathing problems or hoarseness. The enlarged thyroid can also cause pressure symptoms in the neck. Sometimes an enlarged thyroid simply works normally, but it can also happen that it works slower or faste
Causes of thyroid problems
A slow-working thyroid is more common (about 150 in 100,000 people) than a fast-working thyroid (about 40 in 100,000 people). But why does your thyroid get out of balance? There are many possible causes. Often, the cause of the symptoms is in the thyroid itself. There may be a hereditary condition or a tumor in the thyroid. Medications like iodine and lithium can also affect the thyroid’s functioning. In rare cases, the problem lies in the pituitary gland, in the control of the thyroid.

Hashimoto’s disease – an autoimmune disease – can also be the culprit. In that case, the thyroid is inflamed. Over time, this causes the thyroid to work slower.
Too much stress can be a factor in the development of problems; some women also have problems with their thyroid after pregnancy. There is a difference between men and women. Men are less likely to have thyroid problems. Roughly speaking, five times more women than men have problems with their thyroid. Why this is, science has yet to determine.
Related tests



Possible consequences
The long-term consequences of a slow-working thyroid can be profound. There are countless problems associated with hypothyroidism:
- If too little thyroid hormone is produced, this lowers the heart rate. This can lead to heart failure in the long term. A slow thyroid can also cause high blood pressure and increased cholesterol levels in the blood.
- A shortage of thyroid hormone can also cause fertility problems and increase the risk of miscarriage. The unborn baby can also suffer from a lack of thyroid hormone. It can disrupt brain development and lead to low birth weight.
- Among people with a slow-working thyroid, glaucoma is more common. The increased eye pressure associated with glaucoma can lead to blindness.
- Finally, a slow-working thyroid can also change mood. Depressive symptoms are more common in people with disrupted thyroid function.




Cure: with or without medication
A doctor may decide to treat a slow-working thyroid with levothyroxine, an artificial thyroid hormone. Patients often have to take this medication for life. The dosage is different for each patient, so it takes some time for the medication to be properly adjusted.
Many processes in the human body are interconnected. For example, thyroid patients often have an iron deficiency. But that can also be because there is a shortage of vitamin C in the body, because vitamin C stimulates the absorption of iron. Thyroid patients also have a higher chance of vitamin B12 and vitamin D deficiencies. Fortunately, the latter can be easily addressed by taking vitamin D pills.

What to do when experiencing thyroid problems
Many of the complaints related to a slower or faster functioning thyroid can also be associated with other conditions. To be sure, you should visit a GP who can carry out tests, or you can do a home test. The latter is now made easy and fast with the Thyroid Function Home Test from Easly. A few days after the test, you can view the result in a secure environment, which is interpreted and provided with advice by a registered BIG doctor as a standard procedure.