Hemoglobin is a crucial indicator of our health. You will encounter this value almost always when undergoing a blood test. Hemoglobin plays an essential role in transporting oxygen throughout our bodies, making it one of the most important functions in our system. In this blog, we will delve into the function of hemoglobin, the symptoms and causes of both low and high hemoglobin levels, how to determine your hemoglobin levels, and relevant lifestyle tips to keep your hemoglobin as optimal as possible. There is certainly much to discuss about this intriguing protein, so keep reading!
What is hemoglobin?
Hemoglobin is a protein found in red blood cells. Its crucial role is to capture oxygen molecules in the lungs and transport them to all tissues and organs in the body. Oxygen is essential for all processes in our body. In this process, hemoglobin binds to oxygen in the lungs and releases oxygen to the tissues, where it can be used for various bodily functions. Additionally, hemoglobin also plays a role in transporting carbon dioxide, which is a byproduct of our metabolism. Hemoglobin ensures that carbon dioxide is picked up from the tissues and delivered to the lungs, allowing us to exhale and eliminate the waste product. This intricate process is carried out with each breath.
The quantity of hemoglobin is crucial for the proper execution of the mentioned processes. Both too low and too high levels of hemoglobin can cause problems. Later, we will discuss the normal values of a healthy hemoglobin level and how to determine your hemoglobin levels (which can be done easily at home). But first, let’s delve further into the relationship between hemoglobin, iron, and ferritin.

Hemoglobin, ferritin, iron, and anemia: What is the relationship?
The hemoglobin level, also abbreviated as Hb, is measured as part of a general blood test but can also be measured on its own when a doctor suspects either a high or low hemoglobin level. Thus, the hemoglobin level is a crucial parameter when assessing overall health through a blood test. When the hemoglobin (Hb) level is low, we refer to it as anemia; this is called anemia in medical terms
Anemia can be caused by various factors. There may be a deficiency of certain building blocks, such as vitamins and/or minerals, preventing proper hemoglobin production. Additionally, anemia can be caused by chronic diseases or genetic abnormalities. To learn more about the causes of anemia, additional blood tests are conducted, including testing for ferritin, iron, vitamin B12, and folate. Below is an explanation of these different values.
Iron is essential for the formation of hemoglobin. It is a building block of the hemoglobin molecule and aids in binding and transporting oxygen throughout the body. Ferritin is a protein that reflects the iron stores in the body. It is crucial to have sufficient ferritin because a low level may indicate an iron deficiency, hindering hemoglobin production. Vitamin B12 and folate are necessary for the maturation and formation of red blood cells, which contain hemoglobin. Deficiency in these vitamins can lead to disrupted hemoglobin production and ultimately, anemia.
How can hemoglobin be tested?
The measurement of hemoglobin levels can be done through a blood test. A doctor can take a blood sample and have it analyzed in a laboratory. The most common method is hematological analysis, which measures hemoglobin levels and other blood parameters. You can perform this hemoglobin test quickly and easily at home with Easly.
The normal range of hemoglobin varies by gender and age. Additionally, different laboratories may use different normal values. Generally, the normal range for hemoglobin (Hb) is:
– for men, between 9.5 and 11.0 mmol/l
– for women, between 8.5 and 9.7 mmol/l.
The hemoglobin level also changes during pregnancy.

Symptoms and causes of low hemoglobin
As mentioned earlier, hemoglobin plays an essential role in the body. It is responsible for transporting oxygen from the lungs to the tissues and removing the waste product carbon dioxide from the tissues to the lungs. The hemoglobin level is therefore present in the body at a specific level. Both a too high and too low hemoglobin level can cause symptoms. A low hemoglobin level, also known as anemia, occurs much more frequently than a high hemoglobin level.

A low hemoglobin level can lead to various symptoms:
- Fatigue
- Pale appearance
- Heart palpitations
- Shortness of breath
- Weakness
- (Almost) fainting
- Headache
- Ringing in the ears
The most common cause of a low hemoglobin level is iron deficiency anemia. As discussed earlier, iron is a crucial component of hemoglobin. In women, iron deficiency is often caused by heavy menstruation. The body loses too much blood (and iron), resulting in anemia. An inadequate variety in diet, leading to a deficiency in iron, folate, or vitamin B12, can also cause anemia. Additionally, certain diseases, genetic conditions, and specific medications can contribute to anemia. It is essential to identify the underlying cause to provide appropriate treatment.
Related tests



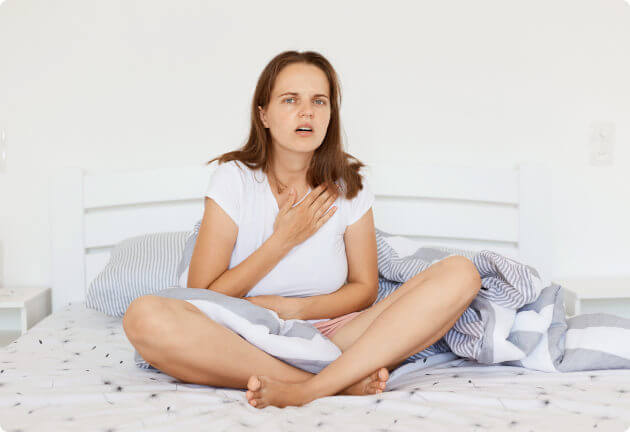
Symptoms and causes of high hemoglobin
While a low hemoglobin level can be alarming, a high hemoglobin level can also be problematic. It is worth mentioning that anemia (a low hemoglobin level) occurs much more frequently than a high hemoglobin level. An excess of hemoglobin can lead to thicker and more viscous blood, increasing the risk of blood clots. This can result in symptoms such as:
- Headaches
- Dizziness
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
- Elevated blood pressure.
Possible causes of a high hemoglobin level include chronic hypoxia (oxygen deficiency), smoking, residence at high altitudes, lung disorders, and certain rare conditions such as polycythemia vera.

How to increase hemoglobin levels?
Now that you understand the importance of maintaining a hemoglobin level that is neither too low nor too high, we provide you with some lifestyle tips for healthy hemoglobin:
- Maintain a balanced diet: To keep your hemoglobin level in check, consume foods rich in iron, such as red meat, poultry, fish, legumes, green leafy vegetables, and whole grains. Vitamin C aids in iron absorption, so ensure an adequate intake of citrus fruits, berries, and other vitamin C-rich foods.
- Avoid excessive caffeine and alcohol consumption, as these substances can hinder iron absorption.
- Regular exercise can stimulate the production of red blood cells.
- Ensure an adequate amount of rest and sleep.




When there is a low hemoglobin level, known as anemia, due to low levels of iron, folate, or vitamin B12, a doctor will often recommend taking supplements to restore the hemoglobin level. The hemoglobin level will gradually rise as a result. This increase is a slow process because you are not directly supplementing hemoglobin but rather a building block of hemoglobin, such as vitamin B12, folate, or iron. When you take these supplements, the body can use the building blocks to produce hemoglobin. The exact duration of this process depends on the initial hemoglobin level and the specific vitamin/mineral deficiency; generally, it may take several weeks to months.



Conclusion
Hemoglobin plays a crucial role in transporting oxygen throughout the body, making it an indispensable part of good health. Both low and high hemoglobin levels can cause problems and symptoms that need to be recognized and treated in a timely manner. With the Easly hemoglobin test, you can easily determine at home whether your hemoglobin level is within the normal range, quickly and reliably. If there is an abnormal result, further investigation will be conducted to identify the specific cause. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is essential for keeping your hemoglobin level in check. It is important to emphasize that we always recommend consulting a doctor if you experience symptoms.