A candida infection can cause a lot of inconvenience and discomfort: from itching and increased discharge to rashes and skin irritation. A candida infection is common and can occur on almost any part of the body. Although it can be a persistent problem, there are fortunately plenty of ways to diagnose and treat this infection. In this blog, we’ll take you through the most common symptoms of a candida infection in both men and women, how to diagnose and treat it, and the best way to prevent a new infection in the future. Keep reading if you want to learn more about Candida infections.
What is Candida?
Candida is a yeast-like fungus that naturally occurs in and on our body, for example in the mouth, throughout the digestive system, and in the vagina. In the normal situation, Candida is present in a certain amount, so that it is in balance with the rest of the (healthy) bacteria and fungi that live in and on our body. This balance is maintained by our immune system and the presence of good bacteria.

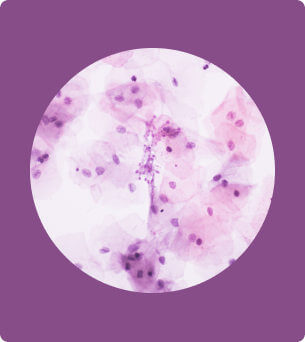
second photo – microscopic image of candidiasis
Various factors can disrupt this balance and cause the Candida yeast to multiply rapidly and cause an overgrowth. The main factors responsible for disrupting this balance are the use of antibiotics, hormonal fluctuations (for example during pregnancy, during menopause, or when using contraception), diabetes, and a reduced immune response. In the normal situation, Candida does not cause any complaints, but when the balance is disrupted and Candida takes over, this can lead to a number of symptoms.
Symptoms of candida infections:
The symptoms you develop due to an overgrowth of Candida depend on the location where the yeast-like fungus is located. Below is an overview of different locations with their corresponding symptoms:
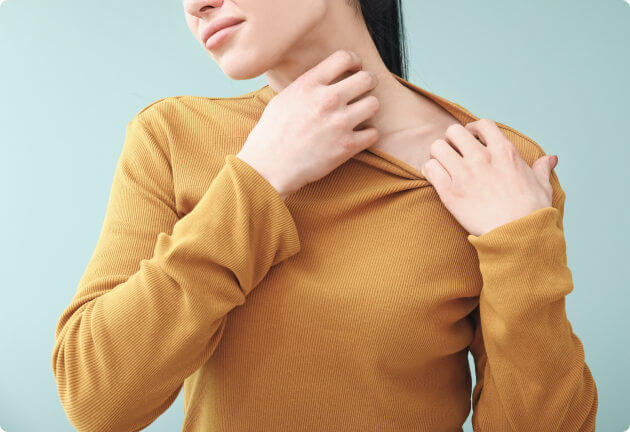
Candida skin infection
Under normal conditions, the Candida yeast also lives on our skin. Due to various factors, such as heat and moisture, the yeast can multiply rapidly. This occurs especially in moist, warm areas such as the groin, under the breasts, between the toes, and in the armpits. Overweight people are also more likely to experience a multiplication of Candida yeast on the skin. The skin becomes red, moist, and sometimes contains blisters. The skin can flake and itch a lot. Below you can see two examples of a Candida skin infection.



Candida infection vagina and penis
In both men and women, the Candida yeast can cause complaints in the genital area. The candida yeast is a normally occurring yeast in the vagina, but can cause complaints when it overgrows. In women, an overgrowth of Candida causes the following complaints: vaginal itching, increased or abnormal vaginal discharge (often white and lumpy), redness and swelling of the labia, and sometimes also pain or burning when urinating. In men, an overgrowth of Candida can cause the following symptoms: redness of the glans, bumps on the glans, flaky skin, and itching around the genital area.


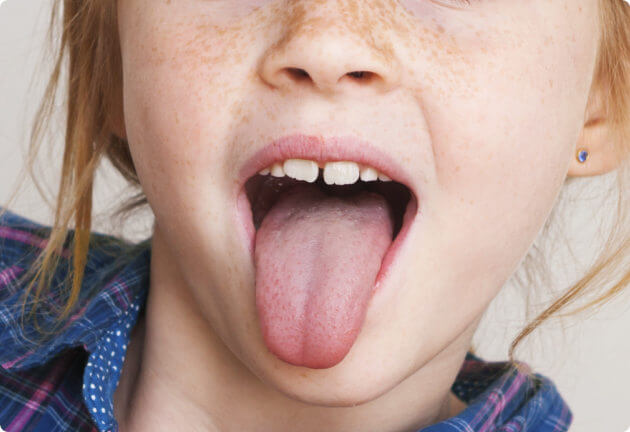
Candida infection oral cavity
This is also called oral candidiasis or thrush. A candida infection in the oral cavity is common in newborns and children, especially when they are still breastfeeding. This is harmless and often goes away on its own. It is characterized by white, creamy spots on the tongue, palate, and inside of the cheeks. This can be painful and cause a burning sensation. In adults, this occurs more often when they use inhalation medication (for example, puffers for asthma) or when there is a reduced immune system.

As mentioned earlier, the Candida yeast occurs in and on our body and does not cause any complaints in this normal situation. The Candida yeast also occurs in our intestines.
In alternative medicine, the Candida syndrome has been discussed more frequently lately; this is a combination of complaints, such as gastrointestinal complaints (abdominal pain, bloating, flatulence) and extreme fatigue. This could then be caused by an overgrowth of Candida. However, it has never been scientifically proven that an overgrowth of the Candida yeast in the intestines could cause these complaints. This disease pattern is therefore not recognized in conventional medicine. It is also strongly discouraged to follow a so-called anti-candida diet. This is again not a scientifically based treatment and can also pose a health risk if there is a shortage of certain foods due to this diet. This is also not recognized as a scientifically based treatment in conventional medicine.
How do you get a candida infection and is a candida infection contagious?
Complaints caused by the Candida yeast are caused by an overgrowth of this yeast. This is caused by a number of factors: by using antibiotics, hormonal changes, diabetes, warm or moist conditions, or a malfunctioning immune system, the candida yeast can overgrow and cause complaints. In principle, it is possible to transmit Candida, for example, through sexual contact, through breastfeeding, or by using the same slippers, clothes, or towel as someone with Candida.




However, Candida is not seen as a contagious disease because the candida yeast is a normal part of the many bacteria and fungi we carry under normal circumstances. Only when you come into contact with a large amount of Candida yeast (such as more frequent sexual contact with someone with a candida infection) can an overgrowth of Candida occur in you as well. However, the most common causes of an overgrowth of Candida remain the aforementioned factors.
How can you test for Candida?
There are several ways to diagnose a Candida infection. Doctors are trained to diagnose a candida infection visually. Specific complaints with specific skin abnormalities on certain parts of the body together give an idea of what infection could be going on. If you are in doubt about the diagnosis or if you want to be sure whether there is a Candida infection, you can easily and reliably test yourself for Candida via Easly. Which test you choose depends on the location where you are experiencing complaints:
Are you suffering from a red, flaky, or itchy skin? And do you want to know if this is caused by a skin fungus like Candida? Take the skin fungus test from Easly, easily and quickly from home.
Are you a woman and has your vaginal discharge changed? Or do you experience itching or discomfort in the genital area? And do you want to know if this is caused by the Candida yeast? Then do the female intimate health test in a simple way.
Related tests

Treatment of Candida infections
A candida infection is treated with local medication, such as anti-fungal cream and/or vaginal fungal tablets. If there is a severe fungal infection, it may be chosen to prescribe an oral treatment with tablets. This choice must always be made by a doctor.

In addition, it is important to prevent a candida infection in the future. The tips below help you prevent a candida infection:
- Keep your skin dry and clean. Candida can multiply rapidly in moist, warm places.
- Lead a healthy lifestyle. This ensures that your immune system works properly, reducing the chance of symptoms from a candida infection.
- Do not wash your vagina with soap. This can change the acidity, making the Candida yeast grow faster.
- Avoid excessive use of antibiotics. This can kill the good bacteria, allowing the Candida fungus to overgrow and cause complaints.
- Choose breathable or airy clothing and shoes, so that there is no accumulation of moisture, making it easy for Candida yeasts to multiply.
- Wear bath slippers in communal areas and avoid prolonged exposure to moist areas, such as swimming pools, jacuzzis, or saunas.
- Do not use the same shoes, clothes, or towels as someone experiencing complaints that could fit a Candida infection.



Conclusion
Candida infections are common conditions that can affect different parts of the body. A diagnosis can be made by a doctor visually or by doing a skin fungus test or genital fungus test. The treatment of candida infections includes antifungal medication and hygiene measures. It is essential to seek professional medical advice and follow the prescribed treatment carefully to effectively combat the infection and prevent complications. Always consult a healthcare provider for a correct diagnosis and treatment of Candida infections.
Sources:
- Maag Lever Darm Stichting – Candida Albicans
- NHG Richtlijnen – Fluor vaginalis
- NHG Richtlijnen – Dermatomycosen
- Soa Aids Nederland – Candida
- Huidziekten – Intertrigo
- Huidziekten – Candida
- Thuisarts – Voetschimmel