Annually, over 100,000 people in the Netherlands get tested for a sexually transmitted infection (STI). But how long does it take for an STI to show up? While chlamydia is the most common STI in the Netherlands, there are numerous others, including gonorrhea, genital herpes, genital warts, syphilis, and HIV. STIs can cause unpleasant symptoms, but they can also progress entirely asymptomatically, meaning you may not experience symptoms but can still be contagious. The speed at which symptoms manifest after infection varies for each type of STI. Understanding the term “incubation period” is crucial, as it influences both the potential diagnosis and treatment. This article delves into the precise meaning of the incubation period, the different incubation periods for various STIs, and the symptoms to expect from each. Keep reading for more information!


What is the incubation period?
The incubation period is the amount of time between the moment of infection and the moment when you first experience symptoms. This is a crucial concept because getting tested for an STI before the incubation period has elapsed is not meaningful. At that point, the disease has not yet manifested, and the test will not provide a reliable answer.
The incubation period varies for different sexually transmitted infections (STIs) depending on the type of STI.
How quickly do you develop symptoms of an STI?
Now that you understand the term incubation period – the time between the moment of infection and the onset of the first symptoms – it’s crucial to be aware of the incubation periods for different STIs. Testing for an STI before the incubation period has elapsed is not meaningful; the STI may still manifest. Some STIs, such as chlamydia and gonorrhea, can cause symptoms within a few days, while others, like HIV and syphilis, may take much longer – sometimes weeks or even months – before symptoms become apparent.
The speed at which symptoms develop varies for each type of STI. The table below illustrates the average incubation period for different types of STIs. The incubation period for oral STIs is comparable to that of genital STIs.
Chlamydia

STI
Chlamydia
Incubation period
1 – 3 weeks
Symptoms
Chlamydia symptoms in women
Asymptomatic
Increased or altered vaginal discharge.
Pain during urination.
Lower abdominal pain.
Vaginal bleeding between menstrual periods.
Vaginal bleeding after sexual contact.
Blood and/or mucus in stool.
Itching and/or irritation around the anus.
Chlamydia symptoms in men
Asymptomatic
Pain or burning sensation during urination.
Discharge from the urethra, especially in the morning.
Pain in the testicles.
Blood and/or mucus in stool.
Itching and/or irritation around the anus.

Gonorrhea

STI
Gonorrhea
Incubation period
2 days to 2 weeks
Symptoms
Gonorrhea symptoms in women:
Asymptomatic
Increased or altered vaginal discharge.
Pain during urination.
Lower abdominal pain.
Vaginal bleeding between menstrual periods.
Vaginal bleeding after sexual contact.
Blood and/or mucus in stool.
Itching and/or irritation around the anus.
Gonorrhea symptoms in men:
Asymptomatic
Pain or burning sensation during urination.
Discharge from the urethra, especially in the morning.
Pain in the testicles.
Blood and/or mucus in stool.
Itching and/or irritation around the anus.
Genital Herpes

STI
Genital Herpes
Incubation period
2 – 12 days
Symptoms
For men and women:
Painful blisters in the genital area.
Pain/burning sensation during urination.
Enlarged lymph nodes.
During the initial infection: very painful blisters, fever, muscle pain.
Mycoplasma

STI
Mycoplasma
Incubation period
Variable, usually after a few weeks
Symptoms
For men and women:
Often no symptoms at all.
Pain or burning during urination.
Men: discharge of pus or mucus from the penis.




Syphilis
STI
Syphilis
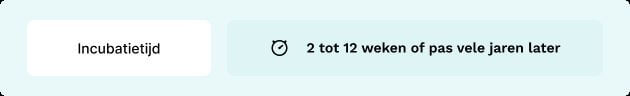
Incubation period
2 – 12 weeks
or even many years later
Symptoms
For men and women:
Stage 1: Red, firm spot/ulcer on the penis, vagina, anus, or mouth. Sometimes this spot may not be easily visible. This spot will disappear on its own.
Stage 2: Subsequently, you may experience general physical symptoms such as fever, headache, enlarged lymph nodes, and skin abnormalities. These symptoms, too, will resolve on their own.
Stage 3: If syphilis remains untreated, it can cause severe symptoms at this stage, which may start up to 30 years after the unprotected sexual contact.
HIV

STI
HIV
Incubation period
2 – 4 weeks
Symptoms
For men and women:
Two to four weeks after infection, flu-like symptoms occur, such as fever, general discomfort, accompanied by a rash. This phase will resolve on its own.
Then follows a phase without symptoms, which can last up to ten years. During this period, the immune system progressively weakens.
If HIV is not treated, the immune system will deteriorate to the point where AIDS develops. AIDS presents a range of symptoms and illnesses and is ultimately (if untreated) fatal.
Trichomonas

STI
Trichomonas
Incubation period
1 – 4 weeks
Symptoms
Trichomonas symptoms in women:
Itching and/or irritation in the vagina.
Different discharge, often green-yellow in color with bubbles.
Red vaginal walls.
Trichomonas symptoms in men:
In men, the infection can proceed without symptoms.
Burning sensation and/or pain during urination.
Related tests

Testing for STIs
As you now know, the incubation period varies for each type of STI. Testing for an STI before the incubation period has elapsed is not meaningful, as the infection may not have manifested yet. Testing before the incubation period can lead to a reassuring result while you are still contagious. Always wait until the incubation period has passed before getting tested for an STI. If the incubation period has elapsed and you want to undergo an STI test, you can do so with ease and reliability at Easly. Use the Easly STI test guide, order your personalized test, and get quick clarity.

Because the incubation period can vary for each STI, and some STIs may not cause any symptoms at all, it’s crucial to get tested regularly if you are sexually active. Sometimes, you can have an STI and transmit it to others even if you don’t have symptoms. That’s why practicing safe sex and regular STI testing are important in preventing the spread of these infections.
Conclusion
The incubation period of an STI is the time between the moment of infection and the onset of the first symptoms. Understanding the incubation periods for different STIs is crucial, as this period not only influences when you may experience symptoms but also determines the right time to undergo an STI test. STIs can be deceptive because they can progress asymptomatically, meaning you may not have noticeable symptoms but can still be contagious, unknowingly infecting others. Practicing safe sex and getting regularly tested for STIs are essential to prevent the spread of these infections and safeguard your own health.